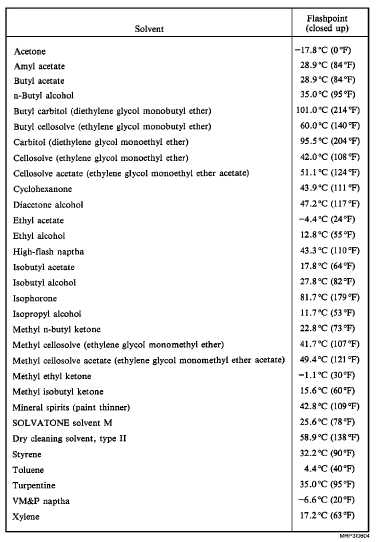
points (lowest temperature at which vapors ignite in air
when exposed to flame). Figure 6-4 shows a list of
commonly used solvents approved by the Navy and the
flash points of these solvents. OPNAVINST 5100.19
(Series) describes proper stowage, handling, and
disposal of these solvents.
Most cleaning solvents contain toxic substances.
These substances can cause injuries if they are inhaled,
absorbed by the skin, or ingested. All toxic materials
must be handled carefully to prevent injury. The
following paragraphs contain information about two
general categories of toxic cleaning solvents. There is
another type—fluorocarbon refrigerants and solvents;
however, special approval is required to obtain and use
them. If you have any questions about the solvent you
are going to use, check the maintenance requirement
cards (MRCs) for the task; ask your supervisor; or
check the NSTM, chapters 631 and 670.
C H L O R I N A T E D - C L E A N I N G
SOLVENTS.—Chlorinated-cleaning solvents can be
highly toxic if used improperly. They may be irritating
to the skin and toxic if ingested. Toxic vapors may cause
damage to the lungs, eyes, and nervous system when the
vapors are present in confined spaces, in spaces with
inadequate ventilation, or when the vapor concentration
is increased by heating. Solvents decompose at high
temperatures and produce gases more toxic than the
solvents themselves. Solvents react with alkalies,
oxidizers, and powdered metals to produce toxic gases.
Common types of chlorinated-cleaning solvents
are trichloroethane (inhibited methylchloroform),
trichloroethylene,
tetrachloroethane,
and
tetra-chloroethylene (perchloroethylene, dry-cleaning
solvent). Because of the extreme dangers involved, the
Navy severely restricts the use of these solvents. For
detailed restriction information on solvents, refer to
NSTM, chapter 670, section 3.
6-9
Figure 6-4. Approved Navy solvents.