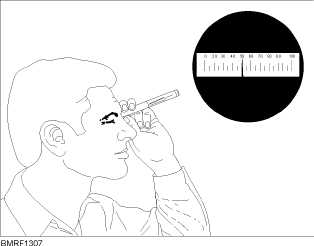
look through the eyepiece; the total radiation dose
received is read directly on the scale. After each use, the
dosimeter is recharged and the indicator line set to zero.
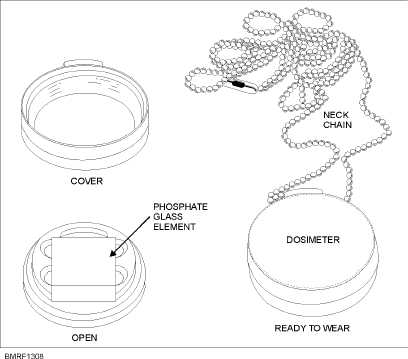
The nonself-reading category is a high-range
casualty dosimeter (fig. 13-8). To determine the total
amount of gamma radiation the wearer has been
exposed to, it’s put in a special radiac
computer-indicator. Its range is 0 to 600 roentgens.
BIOLOGICAL AGENTS
No simple or rapid method can be used to detect
BW contaminants. The only known method consists of
two phases—a sampling phase conducted by a CBR
survey team and a laboratory stage conducted by
medical personnel.
Samples of material are taken from a wide area.
Samples include air, surfaces of bulkheads and decks,
clothing, equipment, water, food, or anything else
suspected of being contaminated. Then the samples are
shipped to a medical laboratory for identification of the
agent.
CHEMICAL AGENTS
Warning of a CW attack based on detection by the
physical senses alone is not only dangerous but would
probably be too late. This is particularly true if
fast-acting nerve agents were used. Special detection
equipment, such as the M256A1 vapor sample detector
kit and the M8 and M9 liquid chemical agent papers, is
used to detect CW agents. Also, draeger tubes are used
to detect the presence of phosgene gas. Other pieces of
13-16
Student Notes:
Figure 13-7.—Self-reading pocket dosimeter.
Figure 13-8.—High-range casualty dosimeter, DT-60/PD.