3. Avoid dry, starchy, and highly flavored foods
and meats if you have less than 1 quart of water
for each day. Remember eating makes you
thirsty. Eat food high in carbohydrates, such as
hard candy and fruit bars.
4. Keep strenuous work to a minimum. The less
you work, the less food and water you require.
5. Eat regularly if possible—don’t nibble. Plan one
good meal each day and cook it if you can.
Cooking makes food safer, more digestible, and
better tasting. Also, the time you spend cooking
will give you a rest period in which you can
relax.
6. Always be on the lookout for food. With few
exceptions, everything you see that walks,
crawls, swims, or grows from the soil is edible.
Learn to live off the land.
PLANTS.—Experts estimate that about 300,000
classified plants grow on the earth’s surface, including
many that grow on mountain tops and ocean floors. Of
these, 120,000 varieties are edible. Obviously, you
won’t be able to learn about all of these plants from
reading this chapter. But if you know what types of food
to look for in the area in which you are stranded, can
identify them, and know how to prepare them properly,
you should find enough to keep you alive. You may even
surprise yourself with a delicious meal.
Eat those plants available in the area to provide you
with needed energy while you search for meat. You can
depend on them to keep you alive if you’re injured,
unarmed in enemy territory, or in an area where wildlife
is not abundant. Although plant food may not provide a
balanced diet, especially in the Arctic where
heat-producing qualities of meat are essential, it will
sustain you. Many plant foods, like nuts and seeds, will
give you enough protein for normal efficiency. In all
cases, plants provide energy and calorie-giving
carbohydrates.
Most sources of plant foods (fruits, nuts, and
berries) have one or more parts that have a lot of food
value. For example, certain roots and other underground
parts of plants that are rich in starch are excellent
sources of food. Some examples are shown on the
following page.
ANIMALS.—Foods derived from animals have
more food value per pound than those derived from
plants. Learning what parts of animals you can eat or
use in other ways and learning how to prepare animals
for cooking increase your chances of survival.
Methods of Cooking and Preserving Foods
Besides making most foods more tasty and
digestible, cooking makes them safer to eat by
destroying bacteria, toxins, and harmful elements in the
food. Your survival chances increase as your knowledge
of field survival skills increases. Survival skills include
your ability to improvise and to apply the following
principles of cooking and preserving the foods you
obtain in the field.
Harmful Plant and Animal Foods
Although you will encounter relatively few
poisonous plants and animals, you should learn to
recognize and avoid them.
Some places, such as the Arctic and subarctic
regions, have less than a dozen plants that are
poisonous. These include the water hemlock (fig.
15-16) and the poisonous mushrooms (figs. 15-17 and
15-18).
15-19
Student Notes:
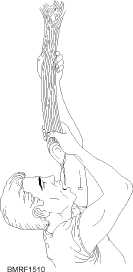
Figure 15-10.—Extracting water from vines.