Two types of surveys are usually conducted—a
rapid, or gross, survey and a detailed survey.
The rapid survey is a preliminary reconnaissance.
Limited numbers of readings are taken in a minimum
amount of time. The purpose of the rapid survey is to
obtain a quick estimate of radiation levels at specified
locations to determine the possibility of keeping
stations manned.
A detailed survey is used to determine the
effectiveness of decontamination measures. All
accessible areas and equipment are surveyed in a slow,
methodical manner. Special attention is paid to areas
that tend to hold contamination (rust spots, caulking in
wood decks, canvas, rope, and so on).
Each member of a monitoring team wears a
protective mask and clothing and is equipped with both
a pocket dosimeter and a high-range casualty dosimeter.
No member with an open cut or wound should enter any
contaminated area. Smoking, drinking, and eating are
prohibited in contaminated areas.
CBR CONTAMINATION MARKERS
A standard system is used to mark areas
contaminated by CW, BW, or nuclear agents. Look at
figure 13-6, which shows CBR contamination markers.
The markers are triangular in shape, with a base of
approximately 11 1/2 inches and sides of about 8 inches.
Each type of contamination is readily identified by the
color of the marker. Additionally, they are labeled GAS,
BIO, or ATOM, as appropriate. The front of the marker
indicates the safe limits of the contaminated area. Never
go beyond the markers without permission. The front
of each marker also contains information about the
contaminated area, such as the date and time of
detection and the type of agent.
NUCLEAR RADIATION
When a ship is exposed to radiation or is
radiologically contaminated (such as from a base surge
or fallout), surveys are made to determine the degree of
contamination.
During surveys, two types of measurement are
made—intensity (dose rate) of the radiation field and
the total amount (dose) received. This information is
used to calculate (find) the safe entry time (time after
exposure when an area may be entered safely) and stay
time (length of time a person may remain in an area
without exceeding permissible radiation exposure
levels). Dose rate is expressed in roentgens (gamma ray
measurement only). The total dose is expressed in rads
(any type of radiation).
One measurement instrument is the radiac meter
(radiac stands for radioactivity detection, indication,
and computation). Usually, only qualified damage
control (DC) personnel use the radiac meter; therefore,
only the personnel dosimeter is covered here.
Measurements are made using two basic types of
personnel dosimeters—self-reading and nonself-
reading.
The self-reading pocket dosimeter (fig. 13-7) is
about the size and shape of a fountain pen and comes in
the following ranges:
0 to 5 roentgens
0 to 200 roentgens
0 to 600 roentgens
0 to 200 milliroentgens
Self-reading instruments measure exposure to
radiation over a period of time, not dose rates at any
given time. Hold the dosimeter up to a light source and
13-14
Student Notes:
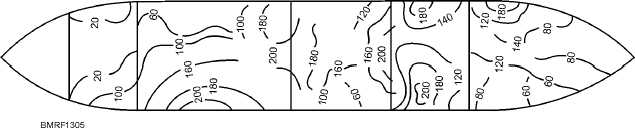
Figure 13-5.—General outline of contaminated areas on weather decks.